What are quick assets list?
bank account

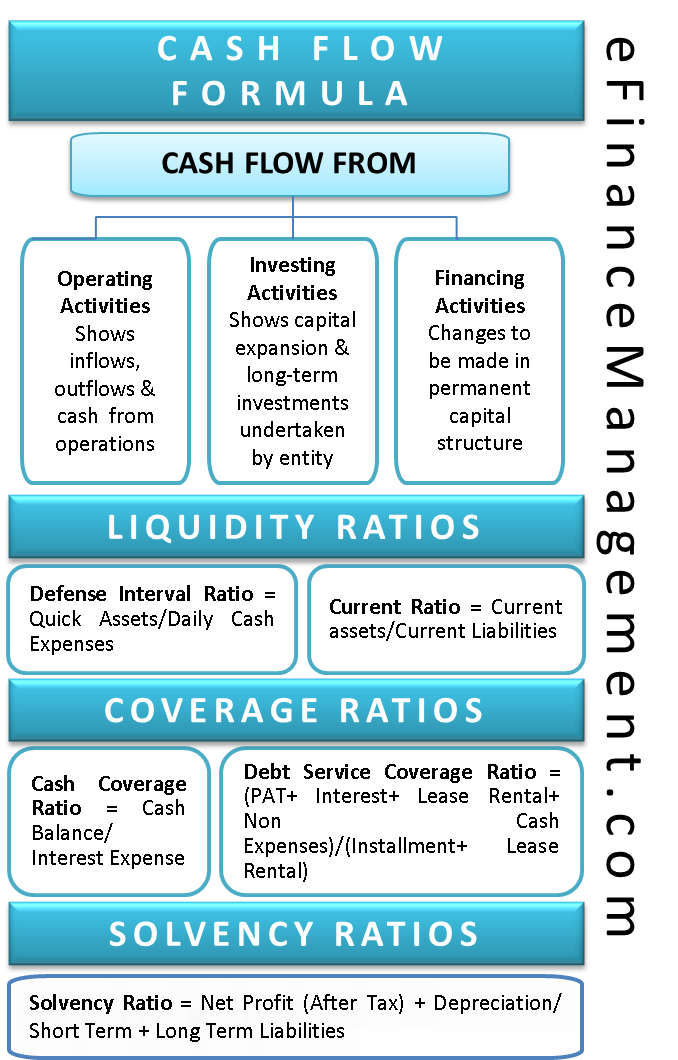
Thequick ratiois a liquidity ratio that compares fast belongings to current liabilities. A quick ratio of .5 means that the corporate has twice as many current liabilities as fast assets. This means so as to pay off all the present liabilities, this firm must sell off some of its long-term belongings.
What are quick assets list?
Quick assets are assets that can be converted to cash quickly. Typically, they include cash, accounts receivable, marketable securities, and sometimes (not usually) inventory.
The monetary accounting time period quick asset is used to explain a subset of present assets used in the calculation of the short ratio, also known as the acid test. Quick assets embody those belongings that may fairly be used to pay present liabilities.
Prepayments are subtracted from current property in calculating fast ratio as a result of such payments can’t be easily reversed. Inventories are also excluded as a result of they don't seem to be instantly convertible to money, i.e. they lead to accounts receivable which in flip ends in money flows and because their web realizable worth drops when they are bought in panic situation.
Related Terms
The fast ratio is an indicator of a company’s short-term liquidity position and measures an organization’s ability to fulfill its quick-time period obligations with its most liquid belongings. Since it indicates the corporate’s capability to instantly use its close to-money belongings (belongings that may be converted quickly to cash) to pay down its current liabilities, it is also referred to as the acid take a look at ratio.
The fast ratio considers only assets that may be converted to cash in a short time. The present ratio, on the other hand, considers inventory and prepaid expense property. In most corporations, stock takes time to liquidate, though a number of rare firms can flip their inventory quick sufficient to think about it a fast asset. Prepaid expenses, although an asset, can't be used to pay for current liabilities, in order that they're omitted from the quick ratio. To calculate the quick ratio, locate every of the formulation components on a company's balance sheet in the current assets and current liabilities sections.
Quick Assets
The fast ratio measures a company's liquidity by trying only at an organization's most liquid assets and dividing them by present liabilities. "Quick" assets are cash, shares and bonds, and accounts receivable (i. e. , all present property on the stability sheet besides inventory). zero are often thought-about passable if receivables assortment is not expected to slow. The fast ratio measures an organization's capacity to satisfy its brief-term obligations with its most liquid belongings. It considers money and equivalents, marketable securities, and accounts receivable (but not the inventory) towards the present liabilities.
What Are Quick Assets?
Liquid belongings are the belongings already in money kind or that a can rapidly be converted to money. It can indicate to managers and buyers what assets an organization has to repay liabilities that may abruptly come due. Liquid assets by definition embody money, money equivalents, actively traded investments and accounts receivable.
Of course, this can depend upon the sort enterprise and the kind of the current property and present liabilities. A very excessive current ratio would possibly imply that cash readily available isn't getting used efficiently. For example, it could be an excellent time to invest in up to date tools for higher productiveness.
Analysts most often use quick property to assess an organization's capability to fulfill its instant bills and obligations which might be due within a one-year interval. This ratio permits investment professionals to determine whether an organization can meet its monetary obligations if its revenues or money collections happen to decelerate. In finance, the short ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio is a kind of liquidity ratio, which measures the ability of a company to use its near cash or quick belongings to extinguish or retire its present liabilities immediately.
Are supplies a quick asset?
What are Quick Assets? Definition: Quick assets are assets that can be used up or realized (turned into cash) in less than one year or operating cycle. These assets usually include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, and temporary investments.
With a quick ratio of zero.94, Johnson & Johnson seems to be in a good place to cowl its current liabilities, though its liquid property aren't quite capable of meet each greenback of brief-time period obligations. Procter & Gamble, however, could not be capable of pay off its current obligations utilizing only quick belongings as its quick ratio is nicely below 1, at 0.fifty one. The fast ratio signifies a company's capacity to pay its present liabilities while not having to sell its stock or get further financing. The current ratio measures an organization's capacity to pay brief-time period and long-term obligations and takes under consideration the whole current property (each liquid and illiquid) of a company relative to the present liabilities.
The following ratios are generally used to measure an organization’s liquidity position, with each one using a unique variety of current asset parts against the current liabilities of a company. On thebalance sheet, current property will usually be displayed in order ofliquidity; that is, the gadgets which have a better chance and convenience of getting converted into cash will be ranked greater. Current assets are essential to businesses because they can be utilized to fund day-to-day enterprise operations and to pay for ongoing working expenses. Since the time period is reported as a dollar value of all the assets and sources that may be easily converted to money in a brief time period, it additionally represents a company’s liquid belongings. Since current assets is a normal merchandise showing within the steadiness sheet, the time horizon represents one yr from the date proven within the heading of the company's stability sheet.
img alt="what are quick assets" src="http://cdn0. Illiquid current assets are present belongings which might’t be simply transformed to cash i.e. prepayments, advances, advance taxes, inventories, and so on. While calculating the quick ratio, double-examine the constituents you are utilizing in the formula. The numerator of liquid belongings should embrace the assets that can be simply converted to money in the quick-term (inside ninety days or so) without compromising on their value. Inventory is not included within the fast ratio as a result of many firms, to be able to sell via their inventory in ninety days or much less, must apply steep discounts to incentivize customers to buy shortly. It signifies that the corporate is fully outfitted with exactly enough assets to be immediately liquidated to pay off its current liabilities. Quick ratio is most useful where the proportion of illiquid present belongings to total current belongings is high. However, fast ratio is much less conservative than cash ratio, one other essential liquidity parameter. Quick ratio (also called acid-take a look at ratio) is a liquidity ratio which measures the dollars of liquid current assets out there per dollar of current liabilities. Liquid current belongings are present property which can be quickly converted to money with none important decrease of their value. "Quick" assets are cash, stocks and bonds, and accounts receivable (i. e. , all current assets on the balance sheet except inventory). Cash and money equivalents are a major a part of the liquid property definition as they're the most liquid belongings that an organization holds. This includes checking accounts, money market accounts, financial savings accounts and treasury payments. The liquidity of these belongings is why you begin your liquid belongings formula by including the value of all cash and cash equivalents using the current honest market value. If you make the calculation at the finish of the month, the fair market worth will be the amount of obtainable funds listed on the month-to-month bank statement, web of any fees and charges. Cash and cash equivalents are always included in liquid capital ratio formulation calculations. Liquid present belongings usually embrace money, marketable securities and receivables. A business could have a big amount of money as accounts receivable, which can bump up the short ratio. The liquid assets definition of accounts receivable consists of only what the business expects to gather inside 30 days. Since liquid assets symbolize only property that the business can shortly convert to money, accounts receivable should not embrace any doubtful accounts. This allowance is an estimate of how much of the accounts receivable the corporate believes will not be collected. For example, in case you have $50,000 value of accounts receivables due within 30 days and the allowance for doubtful accounts is 10 percent of receivables, use $45,000 (ninety % of $50,000) in your liquid asset calculation. So long as there is assurance that accounts receivable funds shall be collected inside 30 days, they are often included in a liquid capital ratio method as nicely. A company that has a quick ratio of lower than 1 may not have the ability to totally repay its current liabilities in the short time period, while an organization having a fast ratio larger than 1 can immediately eliminate its present liabilities. For occasion, a fast ratio of 1.5 indicates that a company has $1.50 of liquid assets out there to cover every $1 of its current liabilities. The quick ratio is taken into account a extra conservative measure than the current ratio, which includes all current belongings as coverage for current liabilities. By excluding inventory, and other less liquid assets, the short property concentrate on the company’s most liquid belongings. Quick ratio is a stricter measure of liquidity of an organization than its present ratio. While current ratio compares the entire current belongings to total current liabilities, quick ratio compares cash and close to-cash present assets with current liabilities. Since near-cash current assets are less than whole current assets, fast ratio is decrease than current ratio except all current assets are liquid. Quick ratio’s independence of inventories makes it a good indicator of liquidity in case of firms which have sluggish-moving inventories, as indicated by their low inventory turnover ratio. Quick ratio is calculated by dividing liquid present property by total current liabilities. img alt="what are quick assets" src="https://support. Higher the short ratio more favorable it is for the Company as it exhibits the Company has more liquid assets than the current liabilities. A ratio of 1 indicates the Company has just sufficient property to fulfill the present liabilities whereas the ratio of less than 1 signifies the Company could face liquidity concerns in near time period. Another method to calculation of quick ratio includes subtracting all illiquid present assets from complete present assets and dividing the ensuing determine by total present liabilities. An acid check is a fast take a look at designed to supply instant results—hence, the title. The fast ratio can be contrasted against the present ratio, which is equal to an organization's complete present belongings, together with its inventories, divided by its current liabilities. The quick ratio represents a more stringent test for the liquidity of an organization compared to the current ratio. Current and quick assets are two categories from the balance sheet that analysts use to examine a company's liquidity. Quick assets are equal to the summation of a company's cash and equivalents, marketable securities, and accounts receivable which are all assets that represent or can be easily converted to cash. It is defined as the ratio between rapidly obtainable or liquid belongings and current liabilities. Quick property are present property that may presumably be shortly converted to cash at close to their book values. The fast ratio measures the dollar quantity of liquid assets available against the dollar amount of current liabilities of a company. Quick assets discuss with assets owned by an organization with a industrial or exchange worth that can easily be converted into money or which might be already in a cash type. Quick belongings are subsequently considered to be the most highly liquid belongings held by an organization. They embrace money and equivalents, marketable securities, and accounts receivable. Companies use quick property to calculate sure monetary ratios which might be utilized in determination making, primarily the fast ratio. The fast ratio is more conservative than the current ratio as a result of it excludes stock and other current assets, that are usually harder to turn into money. This could embody essential business bills and accounts payable that need immediate fee. Despite having a healthy quick ratio, the business is definitely on the verge of working out of cash. Current assets include cash, money equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory stock, marketable securities, pre-paid liabilities, and different liquid property. The number of occasions current property exceed current liabilities reveals the company's solvency. It answers the question, "Does my business have enough present belongings to satisfy the cost schedule of present liabilities with a margin of safety?"In common, a robust present ratio is 2 or more. You can calculate it by taking the money on hand and including accounts receivable funds in addition to some other property that may be transformed to money shortly. This complete is then divided by present liabilities, providing you with a ratio of liquid belongings in comparison with current liabilities. Another variation of that is the liquid capital ratio method, additionally called the "working capital ratio" or "present ratio"; it simply makes use of the value of all present liquid belongings divided by all current liabilities.
Why Do Quick Assets Matter?
What are quick assets on a balance sheet?
How it's used by Financial Analysts?
Reading a Balance Sheet
What are quick assets and current assets?
