$ 1.264 3.54%
DeltaChain (DELTA) Rank 4841
| Mkt.Cap | $ 0.00000000 | Volume 24H | 1,555.00DELTA |
| Market share | 0% | Total Supply | 7.5 BDELTA |
| Proof type | N/A | Open | $ 1.22 |
| Low | $ 1.21 | High | $ 1.27 |
DeltaChain

These receptors are expressed almost exclusively by natural killer (NK) cells and play a central role in triggering their activation,but it has been described that γδ T cells can express these receptors.[26] These cells are named NKp46+/Vδ1 IELs. Non-MHC restricted recognition of antigens and high cytokine secretion of γδ T cells suggest that these cells would be effective in cancer immunotherapy. Gamma delta T cells may be considered a component of adaptive immunity in that they rearrange TCR genes to produce junctional diversity and can develop a memory phenotype.
The lymphoid-specific proteins RAG1 (179615) and RAG2 (179616) direct the V(D)J recombination process in both T and B cells. Following synthesis, the gamma and delta chains pair to yield the gamma-delta T-cell receptor heterodimer (Janeway et al., 2005).
UniProtKB
By repertoire analysis of gamma/delta T cells, Davodeau et al. (1994) identified a J delta sequence, TRDJ4, distinct from that of the other 3 TRDJ sequences described by Isobe et al. (1988), Loh et al. (1988), and Satyanarayana et al. (1988). Frequency analysis indicated that TRDJ1 is the most frequently used J delta segment, followed by TRDJ3, and then in turn by TRDJ2 and TRDJ4.
Boehm et al. (1988) described a translocation at the T-cell receptor joining J-delta segment in a human acute T-cell leukemia with a gross chromosomal translocation t(11;14)(p15;q11). The authors hypothesized that the translocation occurred as a result of recombinase error, since the DNA sequence at the chromosome 11 junction is homologous to a recombinase signal sequence. Janeway et al. (2005) summarized the germline organization of the human TCR-delta locus, which is located entirely within the TCR-alpha locus. The 3 D gene segments, 3 J gene segments, and single C gene segment of the delta locus lie, in that order, between the V gene cluster and the J gene cluster of the alpha locus. The delta locus contains 8 V gene segments, each preceded by an exon encoding the leader sequence.

The genes encoding the T-cell receptor delta chain are clustered within the T-cell receptor alpha chain locus on chromosome 14. Unlike other T-cell receptor loci, more than 1 D gene segment may be incorporated into the delta chain, increasing variability. Because the delta locus is located entirely between the V and J segments of the alpha locus, any rearrangement at the alpha locus results in loss of the delta locus.
The antigens recognized by non-Vδ2 T cells expanded in the above infectious contexts have not been characterized, but the fact that Vδ1+ T-cell responses are not blocked by monoclonal antibody directed against known classical or non-classical MHC molecules suggests recognition of a new class of conserved stress-induced antigens. The antigenic molecules that activate gamma delta T cells are still largely unknown. However, γδ T cells are peculiar in that they do not seem to require antigen processing and major-histocompatibility-complex (MHC) presentation of peptide epitopes, although some recognize MHC class Ib molecules.
The major outcome is that the measurement of these cells in blood and skin lesions can be used as a marker in order to follow-up the psoriasis progression. γδ T cells are major T cell subset of intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) present in the epithelial layer of mucosa. They regulate immunosuppressive functions of IELs and play role in development of tolerance.
Your basket is currently empty. i When browsing through different UniProt proteins, you can use the ‘basket’ to save them, so that you can back to find or analyse them later.More...
- In response to IL-23, the adipose gamma T cells will produce IL-17, and this interleukin promotes development and progression of psoriasis.[13] Also it has been proven that Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in patients suffering from Psoriasis participate in the development of the disease.[14] The number of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells increase in the skin lesions of psoriasis patients but decreased in the blood.
- Janeway et al. (2005) summarized the germline organization of the human TCR-delta locus, which is located entirely within the TCR-alpha locus.
- In most instances, the stimuli that trigger Vd1 expansion are not derived from pathogens but instead correspond to endogenous gene products presumably upregulated on infection.

T-lymphocytes recognize antigens via a mechanism that resembles that used by immunoglobulins (Igs; see ) produced by B cells. There are 2 main mature T-cell subtypes, those expressing alpha (see TRAC; ) and beta (see TRBC1; ) chains, and those expressing gamma (see TRGC1; ) and delta chains. Unlike secreted Ig molecules, T-cell receptor chains are membrane bound and act through cell-cell contact. Gamma-delta T cells may also recognize antigens directly without presentation by the major histocompatibility complex.

Furthermore, γδ T cells are believed to have a prominent role in recognition of lipid antigens. They are of an invariant nature and may be triggered by alarm signals, such as heat shock proteins (HSP). .97e-33T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 delta chain; This is an immunoglobulin-like domain. CD3delta and CD3epsilon complex together as part of the T-cell receptor complex. A recent study has identified a specific subset of gut-resident Vδ1 IELs (intraepithelial lymphocytes) which express high levels of a natural cytotoxic receptor (NCR) which is NKp46.
This section provides information about the protein and gene name(s) and synonym(s) and about the organism that is the source of the protein sequence.More...Names & Taxonomyi

Two delta V genes are located near the delta C gene, one just upstream of the delta D gene cluster and the other in inverted orientation just downstream of the delta C gene. The other 6 delta V gene segments are interspersed among the alpha V gene segments. Five of these V genes are shared with the alpha locus and can be used by either locus, whereas the other V gene is unique to the delta locus. After infiltrating tumor as a response to chemokines produced by monocytes and macrophages, γδ T cells interact with stress-induced molecules on tumor cells and secrete cytotoxic molecules, inflammatory cytokines and activate adaptive immunity cells. They can also lyse tumor cells by antibody‐dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) (through binding Fc region of IgG deposited on tumor cells).
These so-called protective γδ T cells promote tissue repair and cell healing. Pathogens and other inflammation stimuli cause production of retinoic acid by dendritic cells, it induces γδ T cells to produce IL-22. This cytokine is responsible for cell-mediated production of antimicrobial peptides and tissue repair. By use of 'chromosomal walking' techniques and by analysis of a translocation t(8;14)(q24;q11) from a T-cell leukemia, Isobe et al. (1988) mapped the TCR-delta locus within the TCR-alpha locus on chromosome 14q11.2.
DeltaChain valuesUSD Price $ 0.0000
Non-Vδ2 γδ T cells are expanded in various infectious contexts involving intracellular bacteria (Mycobacteria and Listeria) as well as extracellular bacteria, such as Borrelia burgdorferi and viruses (HIV, cytomegalovirus). In most instances, the stimuli that trigger Vd1 expansion are not derived from pathogens but instead correspond to endogenous gene products presumably upregulated on infection.
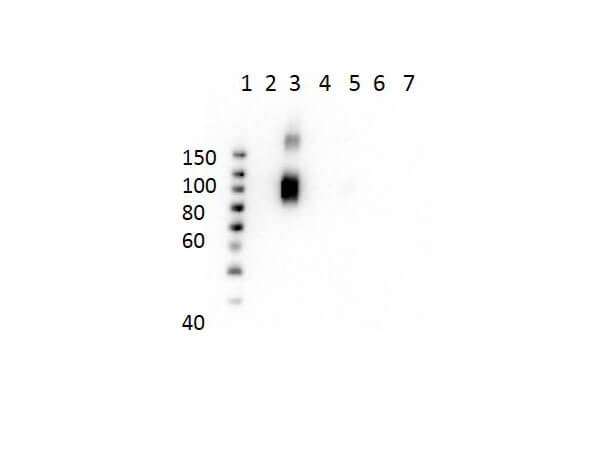
Nitrogenase vanadium-iron protein delta chain
γδ T cells secrete IFN-γ and IL-17, which leads to higher expression of MHC-I, positive regulation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and induction of anti-tumor response. is one of the autoimmune diseases in which the γδ T cells together with Th1 and Th17 play an essential role in the disease development. In response to IL-23, the adipose gamma T cells will produce IL-17, and this interleukin promotes development and progression of psoriasis.[13] Also it has been proven that Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in patients suffering from Psoriasis participate in the development of the disease.[14] The number of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells increase in the skin lesions of psoriasis patients but decreased in the blood. This finding indicates redistribution of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells from the blood to the skin compartment in psoriasis. The psoriasis severity is associated with lower level of γ9Vδ2 T cells in the circulation, therefore a successful anti-psoriatic therapy leads to increase of peripheral Vγ9Vδ2 T cells.







