$ 0.078 1.16%
UCOT (UCT) Rank 4223
| Mkt.Cap | $ 0.00000000 | Volume 24H | 0.00000000UCT |
| Market share | 0% | Total Supply | 1.05 BUCT |
| Proof type | N/A | Open | $ 0.08 |
| Low | $ 0.08 | High | $ 0.08 |
This article presents key criteria and guidelines for the effective layout of UML class and sequence diagrams from the perspective of perceptual theories. Two UML tools are evaluated to illustrate how the criteria can be applied to assess the readability of their generated diagrams. After a few rounds of negotiations, Go Vita decided to join the UCOT family, and the two parties signed an MOU to form a long-term strategic partnership. According to Go Vita, the company will work with the UCOT team to promote the landing of the UCOT ecosystem in its business model. This is to ensure product quality, improve supply chain efficiency, and enhance the consumer experience.
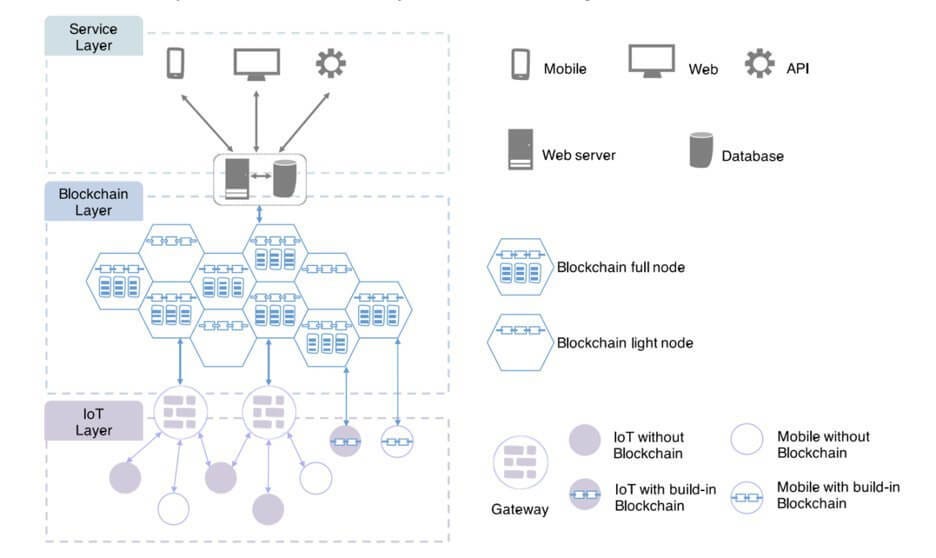
based on IoT, blockchain, 5G, AI and big data.
analyzing the effect of faults on functional requirements during use case analysis. This paper overviews a sys- tematic approach for use case-based modeling of faults and failsafe fault-tolerance, where a failsafe fault-tolerant sys- tem at least meets its safety requirements when faults occur.
Chapter 7 concludes the publication by linking the themes described in the earlier chapters. It represents a way to establish a shared ontology relevant to stakeholders and decision support systems designers.

Log in to Twitter

In model-driven information systems engineering, model transformations reside at the very core of this paradigm. Indeed, model transformations (in particular, model-to-model, or M2M) are a must-have feature of any modern model-driven approach supported by CASE technology. Model transformations are intended to raise quality of the models under development, and also speed-up the modeling itself by bringing in certain level of automation into the development process. The proposed solution consists of two concurrent approaches, namely, automatic and semi-automatic, which may be used selectively to achieve the best expected result. Basic implementation aspects of the solution integrating both approaches are also briefly presented in the paper.
Grammatical parser and Abbott's heuristic are used to process the use cases. User can modify the conceptual model by refining entities and relations, as well as roles for the entities.
While UML use case models is the main subject in this research, the proposed solution may be adopted for other UML and MOF-based models as well. Several approaches have been proposed for the transition from functional requirements to object-oriented design. In a use case-driven development process, the use cases are important input for the identification of classes and their methods. There is, however, no established, empirically validated technique for the transition from use cases to class diagrams.

Product certification is an essential tool for enterprises' brand differentiation strategy, but it is often very difficult to verify the authenticity of the certification. While proving the integrity of the product certificating process is an expensive process, it is sometimes difficult to ensure the validity of the claim even after a painstaking auditing process. On a global scale, there are many areas with a lot of corruption, and noncompliant certificating schemes can in fact further endanger the credibility.

Requirements

The checklist is derived from theories of text comprehension, taken from the Discourse Processing community. First, the approach can be used to derive, or examine further, use case guidelines. That is, by considering whether such guidelines are likely to result in desirable qualities within the resulting description, one is able to make an informed judgement about the utility of those guidelines. Second, one can test for the desirable quality features in existing descriptions, thus enabling empirical validation.

Algorithms and tools have been developed to generate these UML diagrams automatically for program understanding purposes. Many tools, however, often ignore perceptual factors in the layout of these diagrams. Therefore, users still have to spend much time and effort rearranging boxes and lines to make the diagram understandable.
In both experiments, deriving class diagrams from the use cases led to a better structure of the class diagrams. The paper concentrates on a semi-automatic extraction approach by proposing UML2SBVR mapping matrix, extraction algorithm and implementation prototype. An experiment and the evaluation of its results are discussed to prove the usability of the presented approach. This paper describes a prototype of a system to automatically analyze use cases and create a conceptual model based on the analysis.
- After a general level introduction to current trends and challenges in the research domain, operational decision making is considered from several viewpoints.
- An experiment and the evaluation of its results are discussed to prove the usability of the presented approach.
- On a global scale, there are many areas with a lot of corruption, and noncompliant certificating schemes can in fact further endanger the credibility.
- If the use cases are written using subject-predicate-object structure and usage of synonyms is minimized, then the system can produce appropriate conceptualmodel of the use cases, facilitating requirements analysis and domain engineering.
- analyzing the effect of faults on functional requirements during use case analysis.
It has, nevertheless, been reported that this technique leads to problems, such as the developers missing requirements and mistaking requirements for design. An alternative technique is to identify classes from a textual requirements specification and subsequently apply the use case model to validate the resulting class diagram.
Semiautomatic generation of the conceptual model is demonstrated with mixed results. propagate modifications by automated actions and to en- able users to navigate through different models and to de- tect their interrelations. Moreover, RAT integrates require- ments analysis with rationale information to support and capture model negotiations consisting of alternatives, as- sessments, arguments and justifications. RAT is a location independent multi-user tool that supports synchronous and asynchronous group collaboration. Automatically analyzing use case documents is challenging primarily because they are written in natural languages.
In this work, we aim to achieve automatic defect detection in use case documents by leveraging on advanced parsing techniques. In our approach, we first parse the use case document using dependency parsing techniques. The parsing results of each use case are further processed to form an activity diagram. To evaluate our approach, we have conducted experiments on 200+ real-world as well as academic use cases. Ontologies in current computer science parlance are computer based resources that represent agreed domain semantics.
A DOGMA ontology consists of an ontology base that holds sets of intuitive context-specific conceptual relations and a layer of "relatively generic" ontological commitments that hold the domain rules. This constitutes what we shall call the double articulation of a DOGMA ontology 1. UML class and sequence diagrams are helpful for understanding the static structure and dynamic behavior of a software system.

The use cases are based on generic user requirements and address cognitive biases. The specification can be used to set fixed and common terms among the project participants.
The model can be exported to be further utilized with object oriented analysis or domainspecific modeling. The system is evaluated based on the analysis of use cases used to describe the system itself. The quality of models depends essentially on the quality and writing conventions of the use cases. If the use cases are written using subject-predicate-object structure and usage of synonyms is minimized, then the system can produce appropriate conceptualmodel of the use cases, facilitating requirements analysis and domain engineering.
This paper describes two controlled experiments conducted to investigate these two approaches to applying use case models in an object-oriented design process. Half of the subjects used a professional modelling tool; the other half used pen and paper. The second experiment was conducted with 22 professional software developers as subjects, all of whom used one of several modelling tools. The first experiment showed that applying use cases to validate class diagrams constructed from textual requirements led to more complete class diagrams than did the derivation of classes from a use case model. In the second experiment, however, we found no such difference between the two techniques.
Third, as a minimum, the quality features can themselves be used as a checklist for the examination, and revision, of use case descriptions. To demonstrate applicability, the paper reports upon the use, and success, of the approach on an industrial case study. The publication introduces a multidisciplinary approach to operational decision making (operation and maintenance) applied to the Finnish pulp and paper industry. The purpose of the approach is to produce knowledge and methods that support each other and which can be used to improve the support of operational decisions in the declared scope. After a general level introduction to current trends and challenges in the research domain, operational decision making is considered from several viewpoints.
The normative view on operational decision making, introduced in Chapter 2, is based on statistical decision theory. It considers a decision task as an optimisation problem, typically with multiple objectives and uncertainties, and provides a fundamental set of decision making elements. Chapter 3 presents a process monitoring and diagnostics view on operational decision making and describes new data analysis techniques for condensing and combining data.
Chapters 4 and 5 deal with the organisational aspect of operational decision making. Chapter 5 introduces a collaboration view on operational decision making that considers distributed decision making in human actor networks. New standards, technologies and their assignment in a new proposed IT architecture are presented in the Chapter 6. In addition, the information technology development path, from current information systems to new ones, is described.
@UcotMedia
model in Unified Modeling Language in order to decrease inconsistency between them for business Web application development. In this paper, we have compared our proposal with traditional use case modeling to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposal.








