$ 3.029 0.10%
Aditus (ADI) Rank 139
| Mkt.Cap | $ 3.03 B | Volume 24H | 65,023.00ADI |
| Market share | 0% | Total Supply | 0.00000000ADI |
| Proof type | N/A | Open | $ 3.03 |
| Low | $ 3.00 | High | $ 3.07 |
Immensum ad antrum aditus! Enter
Above and posterior to the promontory is the fenestra vestibuli or oval window occupied by the foot-piece of the stapes. Below and posterior to the promontory is the round window or fenestra cochlea. If mastoiditis is suspected, the pus must be drained from the air cells.
However, the status of aditus is not always known unless a mastoidectomy is performed. In this study we try to find out if there is any clinical clue regarding a blocked aditus ad antrum by looking at the tympanic membrane. Fourty-three cases of cortical mastoidectomies were retrospectively studied in this series. Patency of aditus ad antrum was analyzed with respect to presence of myringosclerosis and the status of middle ear mucosa.
The head of the malleus lies in the epitympanic recess, where it articulates with the next auditory ossicle, the incus. The mastoid air cell system acts as a buffer to equalize the pressure changes in the middle ear. When this has been affected by a sclerotic mastoid or the presence of an inflamed tissue in the aditus blocking the aeration of the mastoid air cell system, achieving an aerating mastoidectomy will re establish this physiologic buffer system. But to identify such cases with blocked aditus preoperatively is not easy.

The antrum communicates behind and below with the mastoid air cells, which vary considerably in number, size, and form; the antrum and mastoid air cells are lined by mucous membrane, continuous with that lining the tympanic cavity. ◆There is a gap in the tympanic membrane of rats, which allows communication between the external meatus and the middle ear.
Roof – formed by a thin bone from the petrous part of the temporal bone. It separates the middle ear from the middle cranial fossa. All tympanoplasty procedures with cortical mastoidectomy surgeries done by the primary author in the past 3 years were analyzed retrospectively from the hospital records. Data was obtained regarding presence or absence of myringosclerosis in each of these cases.
It acts to equalise the pressure of the middle ear to that of the external auditory meatus. The tensor tympani originates from the auditory tube and attaches to the handle of malleus, pulling it medially when contracting.
Lateral wall – made up of the tympanic membrane and the lateral wall of the epitympanic recess. The two main parts of the middle ear have been labelled.

Results for "sharedState.searchStore.query"

The head articulates with the incus, and the base joins the oval window. The middle ear can be visualised as a rectangular box, with a roof and floor, medial and lateral walls and anterior and posterior walls. Ruhl CM, Pensak ML. Role of aerating mastoidectomy in non cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media.
Psychological and Physiological Aspects of Hearing

Diseases such as otosclerosis and otitis media result in conductive hearing loss by affecting the efficiency of the ossicle movement. Otosclerosis, the cause of middle ear conductive hearing loss in about half of cases, may be an inherited disease and is characterized by tissue overgrowth and resultant fixation of the stapes in the oval window.

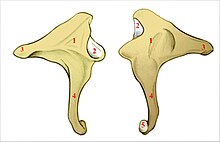
- It is stirrup-shaped, with a head, two limbs, and a base.
- The middle ear lies within the temporal bone, and extends from the tympanic membrane to the lateral wall of the inner ear.
- is an air chamber; it contains a chain of movable bones which transmit the vibrations of the tympanic membrane across the cavity to the middle ear.
- The next bone – the incus – consists of a body and two limbs.
Of 168 ear ossicles, 33.9% showed lesions and prevalence was higher in younger children, and those residing in the urban areas. They noted difficulties in examining the stapes due to its delicate structure and the more common involvement of the incus, especially the long process. The mastoid air cells lie within the mastoid process, opening into the mastoid antrum. In infancy they do not exist and the infantile type of mastoid (without air cells) may persist into adult life in about 20% of people.
Bones
In this study myringosclerosis was found to be significantly associated with a blocked aditus while no such association was found with the status of middle ear mucosa. The presence of myringosclerosis may indicate a blocked aditus ad antrum and performing a cortical mastoidectomy in such cases may help in creating an aerated mastoid, thereby possibly reducing the recurrence rate. The mechanical stiffness of the ossicle chain acts to compensate for the difference in impedance between air and fluid environments (a function called impedance matching) so that there is optimal transfer of energy between the two media. The stiffness of the ossicle chain can also be modified by two muscles of the middle ear, the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles (middle ear reflex).
The duration of the disease in both the groups were similar and ranged from 1 to 15 years. A total of 43 cortical mastoidectomy cases were included in this study. There were no revision cases involved in this study. The outcome of surgery whether graft uptake or hearing improvement was not evaluated, as this was not included in the objectives of this study.
Parts of the Middle Ear

Operative notes of all these cases were reviewed as to the presence or absence of a patent mastoid antrum. Patent mastoid antrum was defined as those ears that showed easy flow of irrigated saline between middle ear and mastoid on reaching the antrum, without the surgeon being required to clear any disease to make it patent. The status of middle ear mucosa was also noted as to whether it was congested or polypoidal, in which case it was termed unhealthy; or normal and healthy.

Kuzinellus aditus
This article will focus on the anatomy of the middle ear– its structure, neurovasculature, and its clinical correlations. Holmquist J, Bergstrom B. The mastoid air cell system in ear surgery. Pinar E, Sadullahoglu K, Calli C, Oncel S. Evaluation of prognostic factors and middle ear risk index in tympanoplasty. This study involved 43 cases of cortical mastoidectomies performed during 2007 to 2010. The mean age of the patients included in the study was 28 years with the youngest being 13 years and oldest being 55 years.
The stapedius also dampens the movements of the ossicles in response to loud sounds. It arises from the inner wall of the pyramid on the posterior wall and the tendon inserts into the neck of the stapes. The proper functioning of the tympanic membrane is dependent upon equality of air pressure being maintained at each of its surfaces. The tympanic cavity, however, is lined with pneumatised mastoid cells which absorb oxygen and in the absence of a pressure regulating device this would soon give rise to a negative pressure in the middle ear. This function is performed by the Eustachian tube, a slender canal which connects the lower portion of the tympanic cavity to the upper part of the throat.
It opens during the act of swallowing allowing air to enter or leave the middle ear. Additionally it serves to equalise pressure variations which occur with change in altitude, as for example when we climb or descend a hill or fly in an aeroplane. is an air chamber; it contains a chain of movable bones which transmit the vibrations of the tympanic membrane across the cavity to the middle ear. Shaped like a narrow box, its axis has an oblique medial and caudal orientation.

When doing so, care must be taken not to damage the nearby facial nerve. The auditory tube (eustachian tube) is a cartilaginousand bony tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.







