$ 0.000 %
Aureus (AURS) Rank 23633
Aureus is a cryptocurency that is built on a blockchain modeled after the Bitcoin protocol. Aureus derives its value through the Aureus Bitcoin Trust, a fund consisting of Bitcoin held for investment. The initial reserve is 15,000 BTC.
| Mkt.Cap | $ 0.00000000 | Volume 24H | 0.00000000AURS |
| Market share | 0% | Total Supply | 21 MAURS |
| Proof type | Open | $ 0.00000000 | |
| Low | $ 0.00000000 | High | $ 0.00000000 |
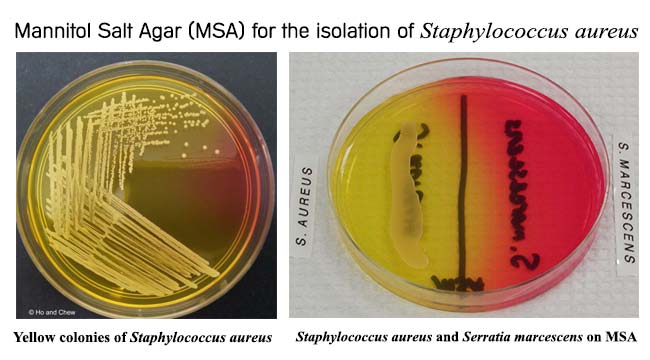
Staph infections
MSA contains an additional indicator for monitoring mannitol fermentation, which makes it a differential media also. Of the bacteria which can grow in the presence of high NaCl, some are halophilic (requiring a certain concentration of salt to grow) while other are haloduric (do not use the salt, but can tolerate it). Staphylococcusis not halophilic, but rather haloduric, in that it can live in or endure high NaCl concentrations. The high salt content in SM1 10 and MSA inhibits other common skin microorganisms. The other media being used in this exercise are for differentiating pathogenic Staphylococcus from nonpathogenic, and for identification of the species.
Laboratories can test to find out which antibiotics will work to kill the bacteria. The major test reaction to use in Staphylococcus identification is the coagulase test reaction, which divides the genus Staphylococcus into 2 groups—coagulase negative species and coagulase positive species. The test media that you will run for identification depends on which category your organism falls in. You may want to run some of the following tests. Novobiocin sensitivity is a key differentiating features among some of the Staphylococcus species.
Healthy people who develop MRSA skin infections rarely develop more serious problems. But people who have weak immune systems and who get HA-MRSA can develop serious, even life-threatening infections.

What does it mean to be Gram positive?
Staphylococcal food poisoning is a gastrointestinal illness. It is caused by eating foods contaminated with enterotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus. The enterotoxins are fast acting, sometimes causing illness within one to six hours. Patients typically experience nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.

These bumps can be red, swollen, and painful and may have pus. Cuts, scrapes, and hairy areas of the body are common places for these bumps to appear. A, Lung sample from a patient with staphylococcal pneumonia showing bronchopneumonia with abscess formation. B, Microabscess with gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus in clusters (×400).
Types of staph infections
aureus (MRSA) strains that are of particular concern for hospital infection control epidemiologists. In light of the increasing incidence of methicillin‐resistant S.
What are the important characteristics of all staphylococcus?
Clinical characteristics of Staphylococcus epidermidis: a systematic review. Staphylococci are known as clustering Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, non-spore forming facultatively anaerobic that classified in two main groups, coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative.

Vancomycin increasingly is required to treat serious staph infections because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant to other traditional medicines. But vancomycin and some other antibiotics have to be given intravenously.
How does Staphylococcus aureus enter the body?
aureus is the most common cause. Streptococci, enterococci, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Escherichia coli are less common. In light of the increasing incidence of methicillin‐resistant S.
This is because MRSA is not killed by certain medicines (antibiotics) used to treat other staph germs. Staphylococcus (staph) is a group of bacteria. A type called Staphylococcus aureus causes most infections. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and drainage of the infected area.

MRSA treatment

Symptoms and signs include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chills. Antibiotics treat pneumonia, and the choice of the antibiotic depends upon the cause of the infection.
Staphylococcal food poisoning is a gastrointestinal illness. It is caused by eating foods contaminated with enterotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus.
The first case of vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (VISA) was reported in Japan in 1996;[97]but the first case of S. Multiple two component signal transduction pathways helps S. aureus to express genes that are required to survive under antimicrobial stress [100]. Cutaneous community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in participants of athletic activities.
- Basically, PIA synthesis induced formation of macroscopically visible, rough cell clusters, whereas Aap- and Embp-dependent biofilms preferentially displayed a smooth layer of aggregated bacteria.
- aureus, 60% of the population will be colonized with S.
- These are deep, infected wounds filled with pus.
- These bacteria are referred to as vancomycin-intermediate-resistance S.
- Microscopically, during the first 48 hours after infection with toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus, the tissue has severe interstitial edema that increases the interalveolar stromal area.
MEDICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA
There are several more potent antibiotics now, but doctors need to know when to use them to prevent further antibiotic resistance. The signs of cellulitis are those of any inflammation -- redness, warmth, swelling, and pain. Any skin sore or ulcer that has these signs may be developing cellulitis. If the staph infection spreads, the person may develop a fever, sometimes with chills and sweats, as well as swelling in the area. Testing the culture will ensure that the correct antibiotic is given for treatment of the infection.
Treatment for bacteremia or blood infection with S. aureus or infection from a medical device – the medical device or the foci of the infection needs to be removed after identification. Of antibiotics β-lactams, oxacillin, nafcillin, cefazolin etc. are preferred. For MRSA vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, Quinupristin/dalfopristin, Cotrimoxazole, Ceftaroline, Telavancin etc. are chosen.
MRSA strains are most often found associated with institutions such as hospitals, but are becoming increasingly prevalent in community-acquired infections. Most of the current research on this bacterium involves the proteomics of Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA. Staph’s resistance to antibiotics has become an increasing problem for today’s society and more research is needed to find our next “super drug”. The Staphylococcus aureus genome, which is the most common species among the Staphylococcus genome projects, is the most completed genome sequence compared to any other microbial species.
Clinical Trials
What are the important characteristics of all staphylococcus?
Staphylococcus (staph) is a group of bacteria. There are more than 30 types. A type called Staphylococcus aureus causes most infections. Bacteremia, an infection of the bloodstream.
When you’re in the hospital, you will be monitored closely and receive powerful antibiotics. These are called “broad-spectrum” antibiotics because they are designed to fight a wide range of infections.
Half the coding sequence is located predominantly on one replichore and the second half is located predominantly on the other replichore. Staphylococci are spherical gram-positive bacteria, which are immobile and form grape-like clusters.
But the infection can spread deeper and affect the blood, bones, or joints. Organs such as the lungs, heart, or brain can also be affected. Serious cases can be life-threatening.
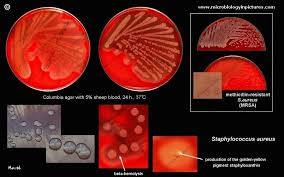
aureus can lay dormant in the body for years undetected. Once symptoms begin to show, the host is contagious for another two weeks, and the overall illness lasts a few weeks. If untreated, though, the disease can be deadly.[29] Deeply penetrating S. This 2005 scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicts numerous clumps of methicillin-resistant S. Staphylococcus is different from the similarly named and medically relevant genus Streptococcus.

However, some staph infections no longer respond to common antibiotics. Staph infections are caused by staphylococcus bacteria, types of germs commonly found on the skin or in the nose of even healthy individuals. Most of the time, these bacteria cause no problems or result in relatively minor skin infections. has emerged as a frequently encountered, life-threatening pulmonary pathogen. Previously seen as a community-acquired complication of influenza, staphylococcal infection is now a primary cause of nosocomial pneumonia, and its evolving drug resistance accounts for methicillin-resistant S.
Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA 300 clone as the predominant cause of skin and soft-tissue infections. 2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreaks of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections--Los Angeles County, California, . Infections by S.aureus are encountered by the nurse practitioner, primary care provider, internist and the infectious disease expert on a regular basis.
epidermidis induced only a diminished inflammatory J774A.1 macrophage response, leading to significantly (88.2 to 88.7%) reduced NF-κB activation and 68.8 to 83% reduced interleukin-1β (IL-1β) production. Mechanical biofilm dispersal partially restored induction of NF-κB activation, although bacterial cell surfaces remained decorated with the respective intercellular adhesins. Our results demonstrate that distinct S. epidermidis biofilm morphotypes are similarly effective at protecting S. epidermidis from phagocytic uptake and at counteracting macrophage activation, providing novel insights into mechanisms that could contribute to the chronic and persistent course of biofilm-related S.
β-Lactam resistance is encoded by an MGE called SCCmec of which there are at least 11 distinct types. No vaccine is available to prevent aStaphylococcus aureusinfection. Careful attention to food-handling and food-preparation practices can decrease the risk of staphylococcal food poisoning. Prevention of staph infections can be aided by proper hygiene when caring for skin wounds. Over 30 different types of staphylococci can infect humans, but most infections are caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
The sample is sent to a lab to test for staph. If staph is found, it will be tested to see which antibiotic should be used to treat your infection. Most staph germs are spread by skin-to-skin contact.

Most strains carry prophages, insertion sequences, transposons and pathogenicity islands. Strains that are resistant to β-lactam antibiotics (methicillin-resistant S. aureus) cause hospital-acquired infections while hypervirulent community-associated MRSA are increasing prevalent.
Sometimes you may need surgery for bone infections. These staph infections range from a simple boil to antibiotic-resistant infections to flesh-eating infections.







