$ 0.043 4.09%
STP Network (STPT) Rank 864
| Mkt.Cap | $ 81.75 M | Volume 24H | 0.00000000STPT |
| Market share | 0% | Total Supply | 0.00000000STPT |
| Proof type | N/A | Open | $ 0.04 |
| Low | $ 0.04 | High | $ 0.04 |
Cisco Switching & Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails. • The Root Switch (Bridge) bridge broadcasts the topology change information into the whole network. The network topology can happen in a network due to different reasons like a link failure, a Switch (Bridge) failure, or a port transitioning to forwarding state. STP uses the Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) to make decisions which switch ports to put on blocking state to prevent loops in your network.
In 2001, the IEEE introduced Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) as 802.1w. RSTP provides significantly faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change, introducing new convergence behaviors and bridge port roles to do this.
What is VTP mode?
The VTP Transparent mode is something between a VTP Server and a VTP Client but does not participate in the VTP Domain. In Transparent mode, you are able to create, modify and delete VLANs on the local switch, without affecting any other switches regardless of the mode they might be in.
This automatic link type setting can be overridden by explicit configuration. RSTP does not do anything differently from STP on shared links. Before creating VLANs on the switch that will propagate via VTP, a VTP domain must first be set up.
We are proud to provide not only top notch certification articles, but also real world scenarios. The PVST+ the bridge ID is composed from a 4 bits bridge priority, 12 bits VLAN ID (VID) and 6-byte MAC address, totaling to a 8-byte BID. Unlike in the original 802.1D standard, the bridge priority is incremented by 4096, not 1. The second field, called Extended system ID is a 12-bit field containing the VID. Finally, the last field in the bridge ID is a 6-byte value, the MAC address.
We will present you the way you will enable PVST+ in this topology. First of all you must decide what switches will be primary and secondary for each VLAN and optionally set the priority to a lower value. Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol Plus (PVST+) was developed by Cisco as a proprietary protocol to provide support for IEEEs 802.1Q trunking. IEEE’s standards are Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and Multiple STP (MSTP). After you decide on the root switch, set the appropriate variables to designate the switch as the root switch.
Cryptography: Understanding Its Not-So-Secret Importance to Your Business
How do you find the root bridge in STP?
Since the BID starts with the Bridge Priority field, essentially, the switch with the lowest Bridge Priority field becomes the Root Bridge. If there is a tie between two switches having the same priority value, then the switch with the lowest MAC address becomes the Root Bridge.
Switches are very important networking devices; they're used to terminate hosts on the LAN. They consist of multiple Ethernet/Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet interfaces with adjustable throughput rates. Switching is the process of using the physical address of devises to perform forwarding decisions.
External links

You can create, modify, and delete VLANs on a switch in VTP transparent mode. VLAN configurations are saved in NVRAM, but they are not advertised to other switches. VTP ClientBehaves like a VTP server, but you cannot create, change, or delete VLANs on a VTP client. VLAN configurations are saved in NVRAM.VTP TransparentDoes not advertise its VLAN configuration and does not synchronize its VLAN configuration based on received advertisements.
In order to further facilitate this view of an MST region as a single RSTP bridge, the MSTP protocol uses a variable known as remaining hops as a time to live counter instead of the message age timer used by RSTP. The message age time is only incremented once when spanning tree information enters an MST region, and therefore RSTP bridges will see a region as only one "hop" in the spanning tree.
What are the values of STP?
STP stands for standard temperature and pressure and it is at a temperature of 0 degrees Celsius or at 273 Kelvin and at a pressure of 101.325 kPa or 1 atm. For gases, at this temperature it was established that for every one mol of a gas it is equivalent to 22.414 Liters.
STP models

How do I stop a Cisco switch from STP?
Although it is not recommended, you can turn off Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a per-VLAN basis, or globally on the switch. Use the no spanning-tree vlan vlan-id command in order to disable STP on a per virtual LAN (VLAN) basis. Also ensure that all switches and bridges in the VLAN have spanning tree disabled.

So SW2 and SW3 compare costs on that segment in the BPDUs sent between each other and one of them has a better cost, in this case SW3. It puts it's port into forwarding and this becomes a DP. To break the loop SW2 must now put it's port into blocking mode. Designated Port - a designated port is one that has been determined as having the best (lowest)cost.

So portfast is fine switch to server, desktop, router, and firewall. Multiple STP (MSTP) allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to the same spanning-tree instance. This way you reduce number of instances required in large networks with a big number of VLANs. MSTP can load balance data traffic because it can provide multiple data paths. Rapid PVST+ is based on the IEEE 802.1w standard but is a Cisco proprietary protocol and has faster convergence than STP.
What is Single Touch Payroll (STP)?
A good practice is to avoid having too many blocking ports. Another good practice is to have no more than two redundant links between to network devices. Another problem that may occur is a too large network diameters. In STP, the network diameter should not be greater than 7, meaning that the longest path between two network devices must not pass more than 7 switches.
- Let’s say that SW1 advertised the lowest switch ID and is elected as the root bridge.
- You can also issue the set spantree portfast command, on a per-port basis.
- Upon receipt of the TCN, the root switch will set the Topology Change flag in its normal BPDUs.
- This switch does not need to be the most powerful switch, but choose the most centralized switch on the network.
- The switch with the lowest bridge ID in the network wins this election process.

An RSTP bridge will "propose" its spanning tree information to its designated ports. If another RSTP bridge receives this information and determines this is the superior root information, it sets all its other ports to discarding. The bridge may send an "agreement" to the first bridge confirming its superior spanning tree information.
With that said, in your scenario, you can enable portfast in all except between the 'switch to switch' connection under normal circumstances. It's used to minimimize the impact of STP TCN BPDU traffic when a simple host is being rebooted or connected to a switch. We hope you found this topic covering the Spanning Tree Protocol helpful in achieving your Cisco CCNA certification.
Since IEEE 802.1D-2004, the first four bits are a configurable priority, and the last twelve bits carry the bridge system ID extension. In the case of MST, the bridge system ID extension carries the MSTP instance number. Some vendors set the bridge system ID extension to carry a VLAN ID allowing a different spanning tree per VLAN, such as Cisco's PVST. Unlike some proprietary per-VLAN spanning tree implementations,[25] MSTP includes all of its spanning tree information in a single BPDU format.
VLAN Trunking Protocol
In the diagram on the right there are two least cost paths from network segment d to the root, one going through bridge 24 and the other through bridge 92. The lower bridge ID is 24, so the tie breaker dictates that the designated port is the port through which network segment d is connected to bridge 24. If bridge IDs were equal, then the bridge with the lowest MAC address would have the designated port. In either case, the loser sets the port as being blocked.
The numbered boxes represent bridges, that is switches in a LAN. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them.
As soon as the bridge detects a BPDU coming to an edge port, the port becomes a non-edge port. When more than one bridge on a segment leads to a least-cost path to the root, the bridge with the lower bridge ID is used to forward messages to the root. The port attaching that bridge to the network segment is the designated port for the segment.
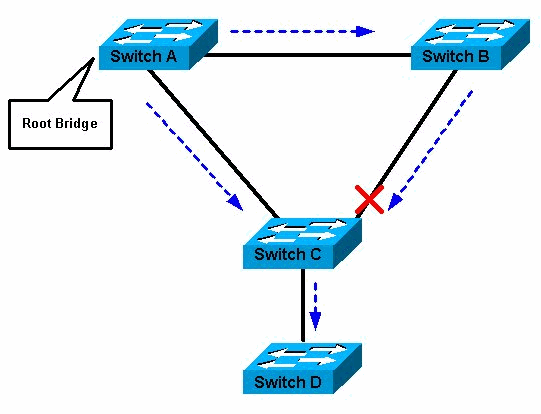
Switch B stops the advertisement of its root ID, and accepts the root ID of Switch A. In this network, a redundant link is planned between Switch A and Switch B. However, this setup creates the possibility of a bridging loop. For example, a broadcast or multicast packet that transmits from Station M and is destined for Station N simply continues to circulate between both switches. In the topology above, STP has placed one port on SW3 into the blocking state. That way, if SW3 receives a broadcast frame from SW1, it will not forward it out the port connected to SW2.
Job Role: Network Administrator
An alternate port offers an alternate path to the root bridge in case the root port fails. This port is in Discarding state until it switches to a designated port.

Transparent switches maintain their own separate VLAN database, and will neither advertise nor accept any VLAN database information from the switches, even a server. One other situation you don't want to enable portfast is if your router has multiple interfaces and they are part of the same bridge group then you don't want to enable portfast on the switchport(s). Although, you mayn't be having this setup it's a good to know that. You don't want to enable porfast in situations that could cause spanning tree loops.
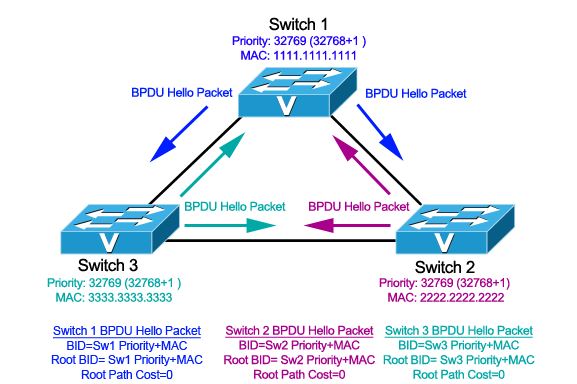
As the BPDU goes out through the network, each switch compares the BPDU that the switch sends to the BPDU that the switch receives from the neighbors. The switches then agree on which switch is the root switch. The switch with the lowest bridge ID in the network wins this election process. When the switches first come up, they start the root switch selection process. Each switch transmits a BPDU to the directly connected switch on a per-VLAN basis.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create loops when you have redundant paths in your network. Let’s say that SW1 advertised the lowest switch ID and is elected as the root bridge. SW2 and SW3 choose ports with the lowest cost to reach the root bridge to be the root ports.

How does STP work in networking?
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is responsible for identifying links in the network and shutting down the redundant ones, preventing possible network loops. In order to do so, all switches in the network exchange BPDU messages between them to agree upon the root bridge. The root bridge needs to be elected.

show spantree portstate —Determines the current spanning tree state of a Token Ring port within a spanning tree. Refer to the Calculating and Assigning Port Costs section of Configuring Spanning Tree for more information on how to calculate the port cost. show spantree vlan_id —Shows the current state of the spanning tree for this VLAN ID, from the perspective of the switch on which you issue the command. Issue the show spantree vlan_id command in order to verify that Switch 15 is the root of all the appropriate VLANs.
Who has to use STP?
Employers with 19 or less employees will need to start using STP between 1 July and 30 September 2019; if your business needs more time to get ready to report through STP, you can apply to the ATO for a deferral.
Issue the set spantree portfast mod_num/port_num enable command in order to configure the PortFast setting on Switches 12, 13, 14, 16, and 17. If Switch A advertises a root ID that is a lower number than the root ID that Switch B advertises, the information from Switch A is better.







